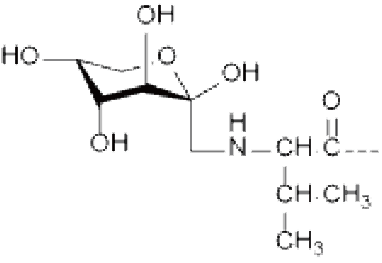
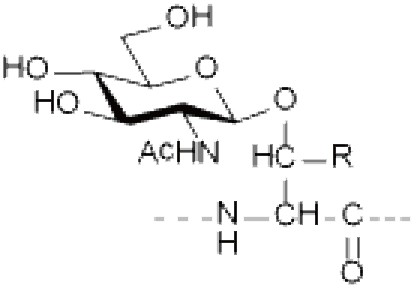Glycosylation modification is the process of connecting monosaccharides or polysaccharides to peptides through chemical bonds. The peptides obtained after glycosylation modification are called glycopeptides. Glycosylation plays a key role in many biological functions, such as protein stability, activity and localization, as well as cell-to-cell recognition and signal transduction. There are two main types of peptide glycosylation: N-linked glycosylation and O-linked glycosylation.
● N-linked glycosylation: occurs on the Asparagine (Asn, N) residue and is one of the most common linkages in nature. Most N-linked glycosylation takes the form of GlcNAc-β-Asn, and there are also forms such as GlcNac-a-Asn and Glc-Asn.
● O-linked glycosylation: occurs on the hydroxyl side chain of amino acids, usually from serine or threonine residues. Most O-linked glycosylation takes the form of GlcNac-B-Ser/Thr or GalNac-a-Ser/Thr.
Case Studies: glycopeptides containing oligosaccharides
Ser/Thr(GlcNAc), Ser/Thr(GalNAc), Asn(GlcNAc), etc.
|
|
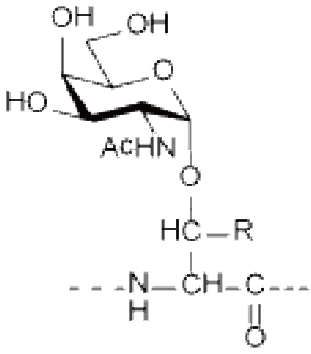
|
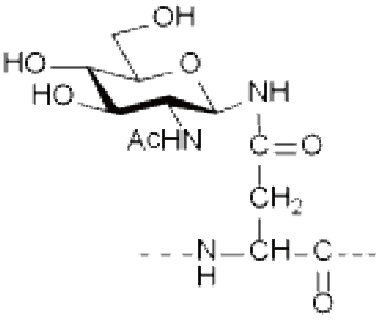
|
|
R=H: Ser(GlcNAc) R=CH 3 : Thr(GlcNAc) O-GlcNAcylation |
R=H: Ser(GalNAc) R=CH 3 : Thr(GalNAc) |
Asn(GlcNAc) |
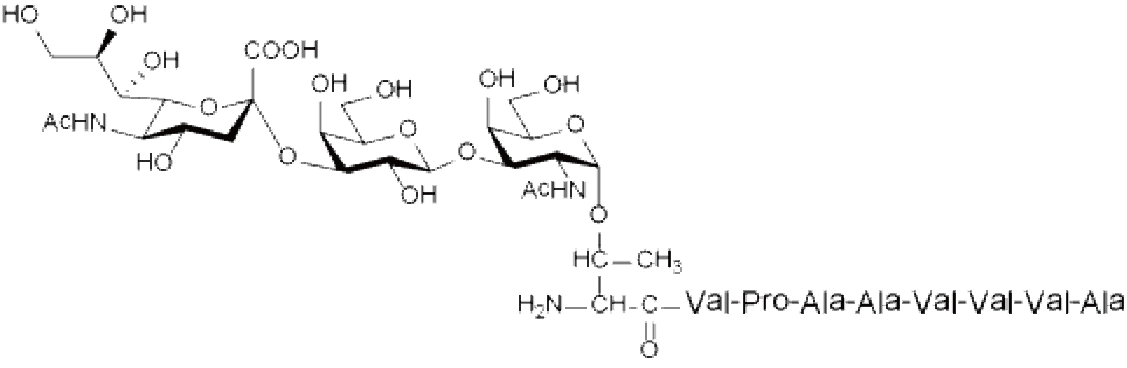
Antiproliferative Factor Sialoglycopeptide (APF Sialoglycopeptide)
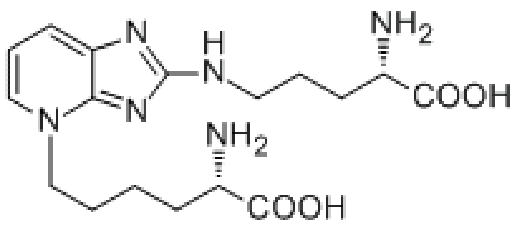
AGEs (advanced glycation end products)
|
|
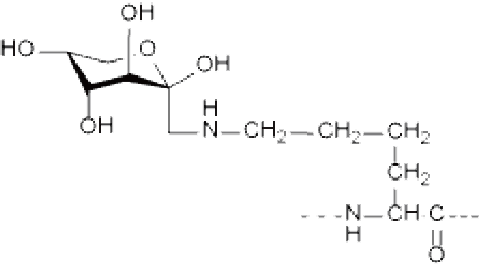 |
 |
| REQUEST A QUOTE | ||
|---|---|---|
| PHONE | ONLINE FORM | |
| [email protected] | +1 408-828-0438 | ONLINE QUOTE SUBMISSION |

 Login
Login Register
Register Contact us
Contact us KR
KR